
First, state the null and alternative hypotheses:īecause you have specified a significance level, you can look up the critical z‐value in Tableī before computing the statistic.
Its scores may be lower than, or higher than, the population of all students taking the test therefore, this problem requires a two‐tailed test. There are two possible ways that the class may differ from the population. Is the class typical of others who have taken the test? Assume a significance level of p < 0.05. A class of 19 students takes the test and has a mean score of 65. In national use, a vocabulary test is known to have a mean score of 68 and a standard deviation of 13.

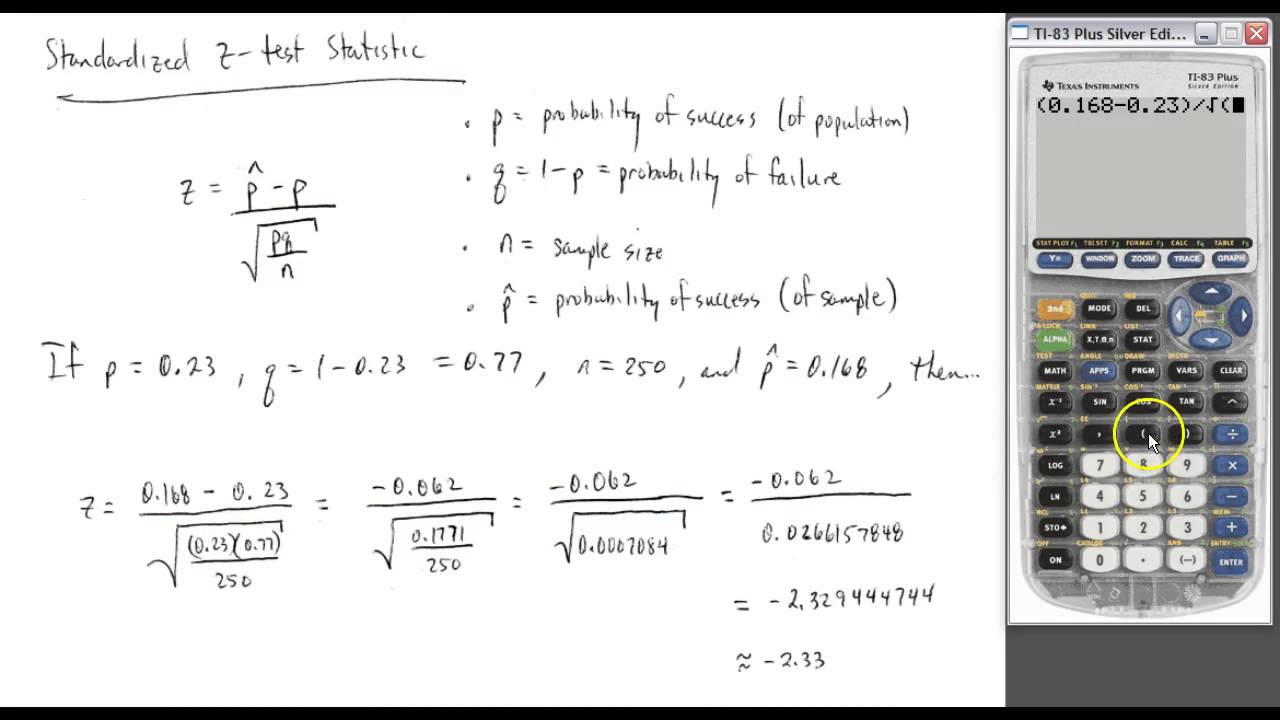
If you had decided beforehand on a significance level of p < 0.05, the null hypothesis could not be rejected. Should the null hypothesis of a weight gain of less than 5 pounds for the population be rejected? That depends on how conservative you want to be. So, the conditional probability that a sample from the herd gains at least 6.7 pounds per steer is p = 0.1003. If the standard deviation of weight gain for the entire herd is 7.1, test the hypothesis that the average weight gain per steer for the month was more than 5 pounds. A random sample of 29 were weighed and had gained an average of 6.7 pounds. Look up the significance level of the z‐value in the standard normal table (TableĪ herd of 1,500 steer was fed a special high‐protein grain for a month. Where is the sample mean, Δ is a specified value to be tested, σ is the population standard deviation, and n is the size of the sample.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
